Pillars Programs of Conservation
Monitoring and Tracking of Habitats
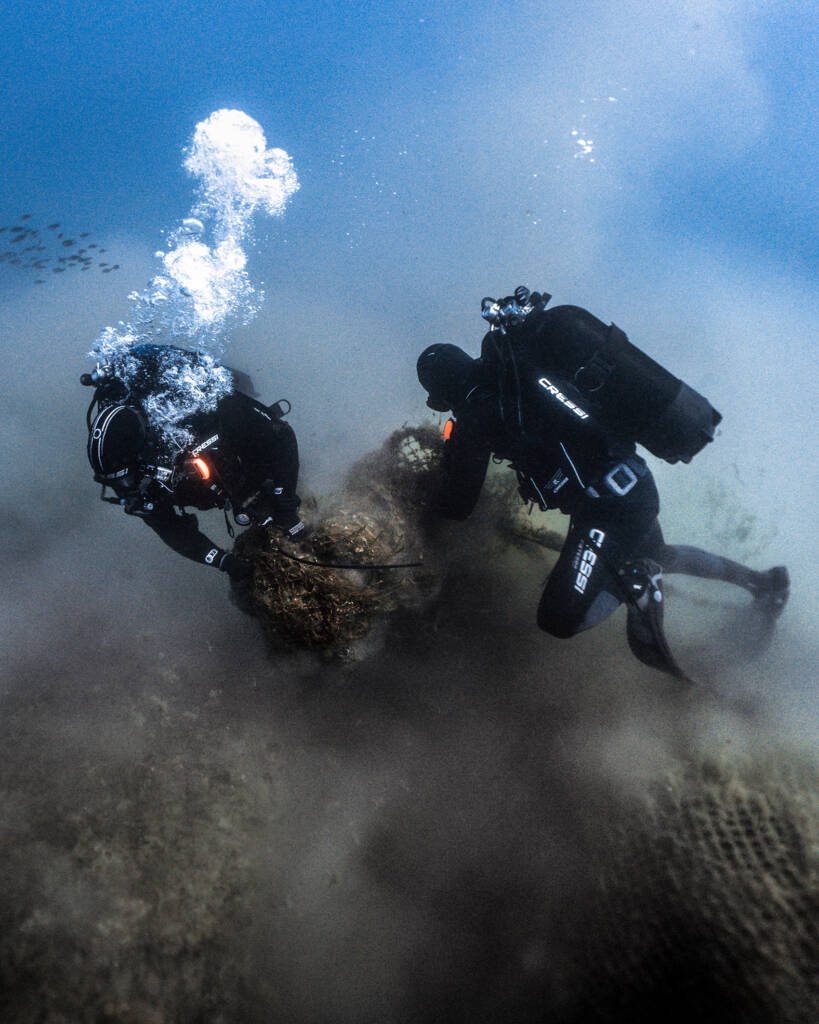

Evaluate marine ecosystems to know their conservation status and identify potential threats
This program includes long-term monitoring projects to anticipate environmental problems and evaluate the effectiveness of conservation measures.
Together, we aspire to strengthen our ecosystems and ensure the survival of vulnerable species.
Lines
-
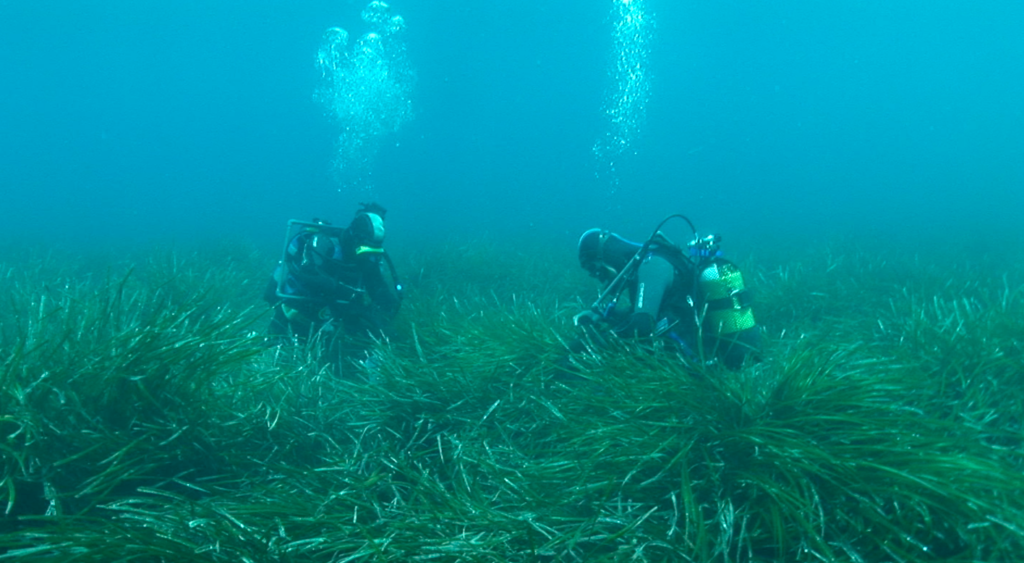
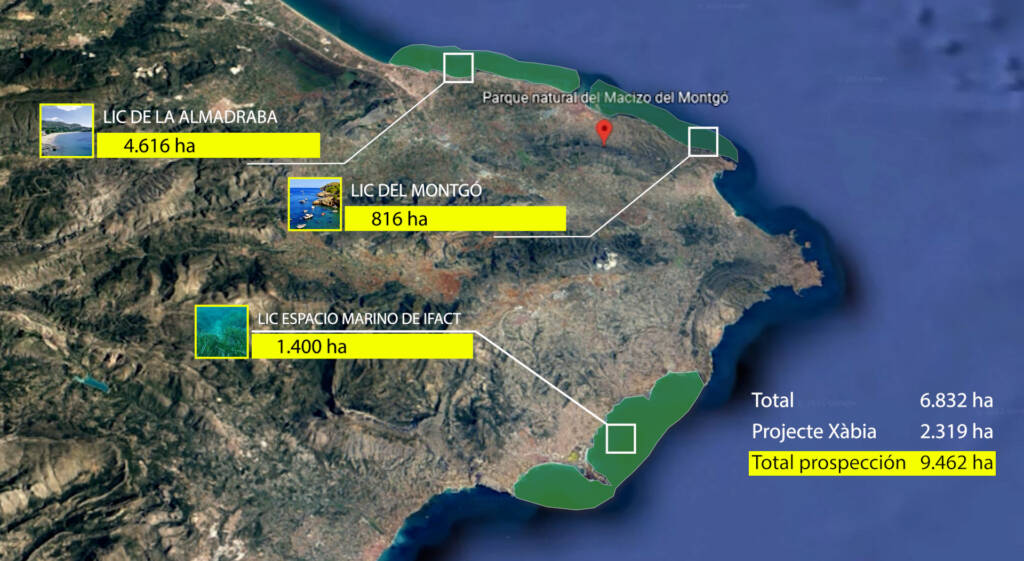
Understanding, interpreting, and conserving marine biodiversity in the Valencian Community
This initiative seeks to involve local communities in understanding and preserving marine wealth. Based on a rigorous scientific method, it aims to value and protect the natural marine heritage, establishing a connection with local stakeholders and communities.
Initially tested successfully in Xàbia (Alicante) and extended to additional municipalities, the proposal now is to advance to new coastal locations with key points of marine biodiversity.
The objective is to broaden the scope to geographical areas such as Marina Alta (Alicante), Oropesa-Benicàssim, and l’Albufera, addressing both high biodiversity and anthropogenic risks. The operation encompasses phases from local documentation and surveying to technical-scientific research to identify and value the heritage. The evaluation of ecological potential, the assessment of human activities, the study of ecosystem services, and the determination of biodiversity indices are key parts of this phase.
The interpretation phase stands out for carrying out education and awareness activities aimed at diverse audiences, from schoolchildren and citizens to tourists and collaborators.







-
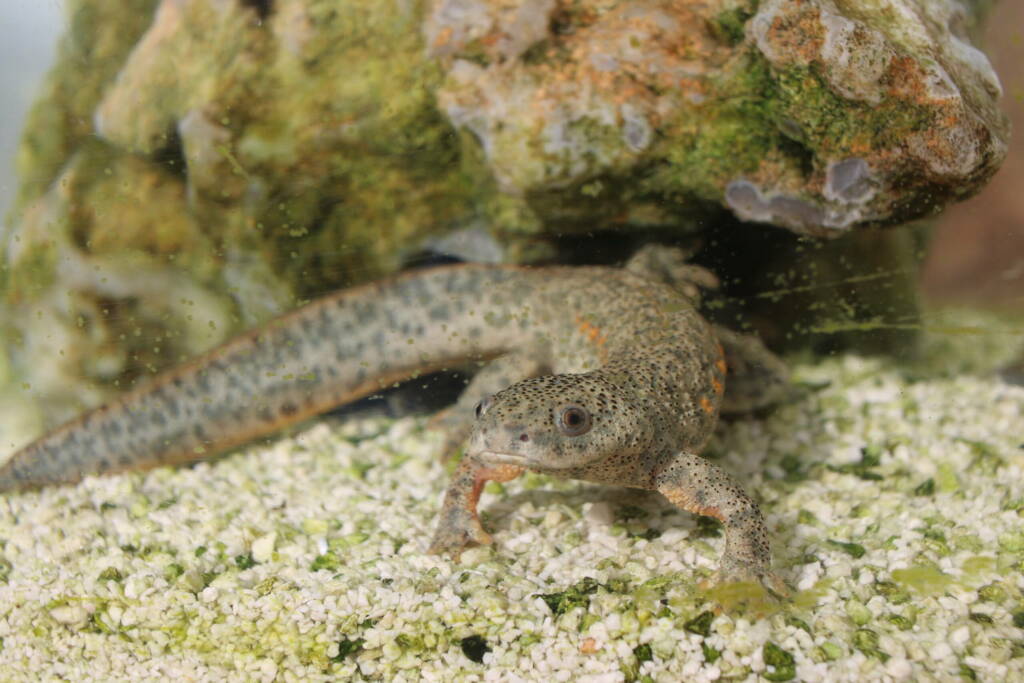
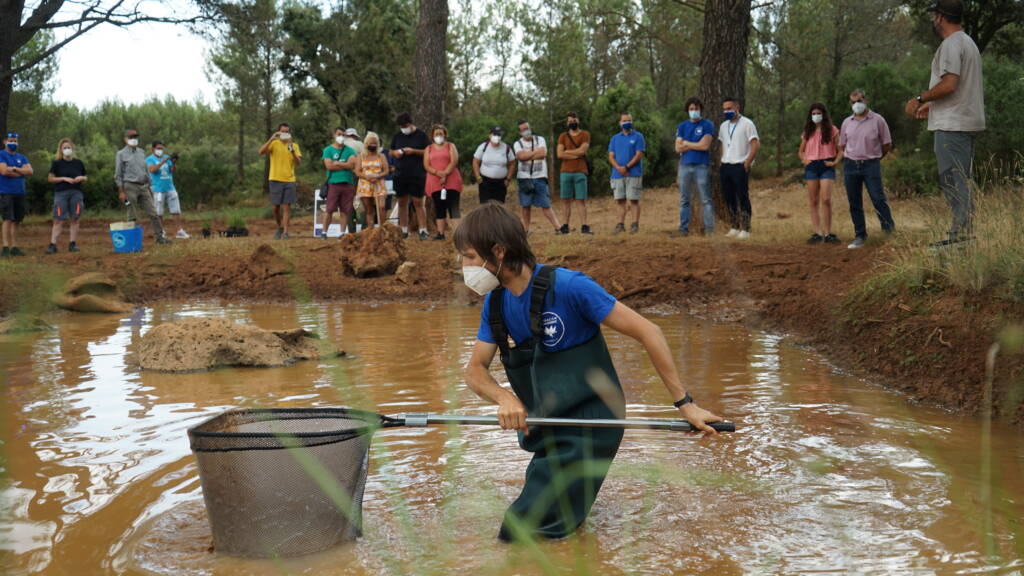
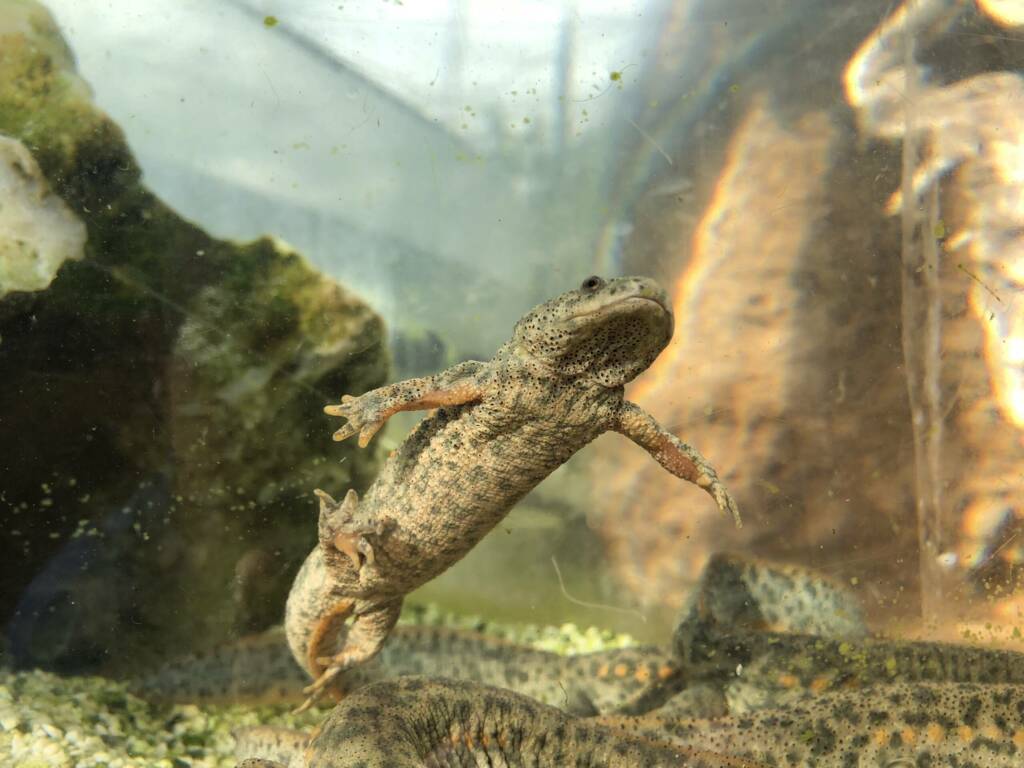
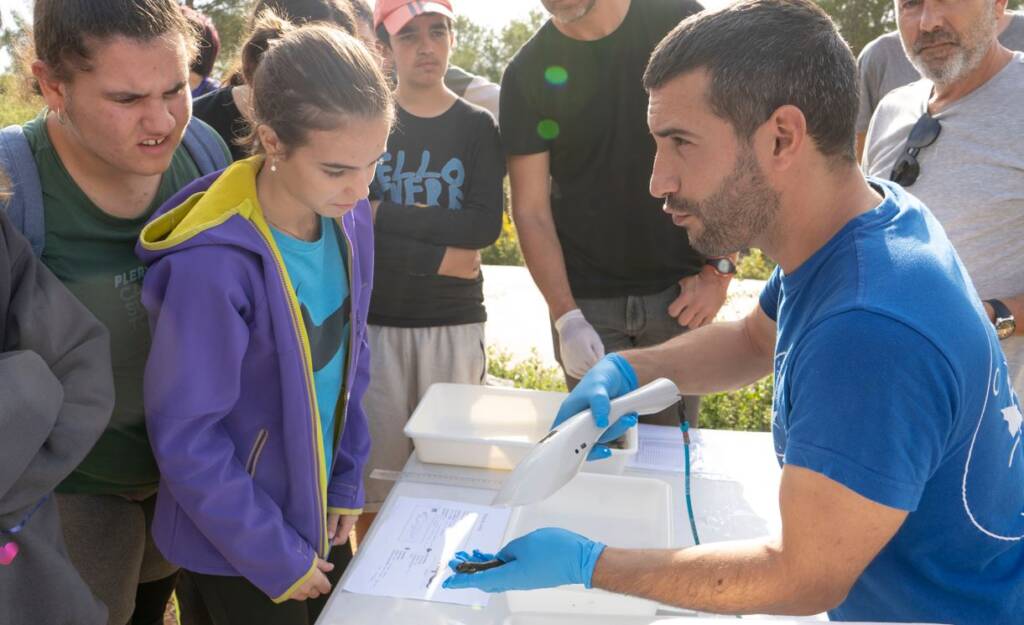
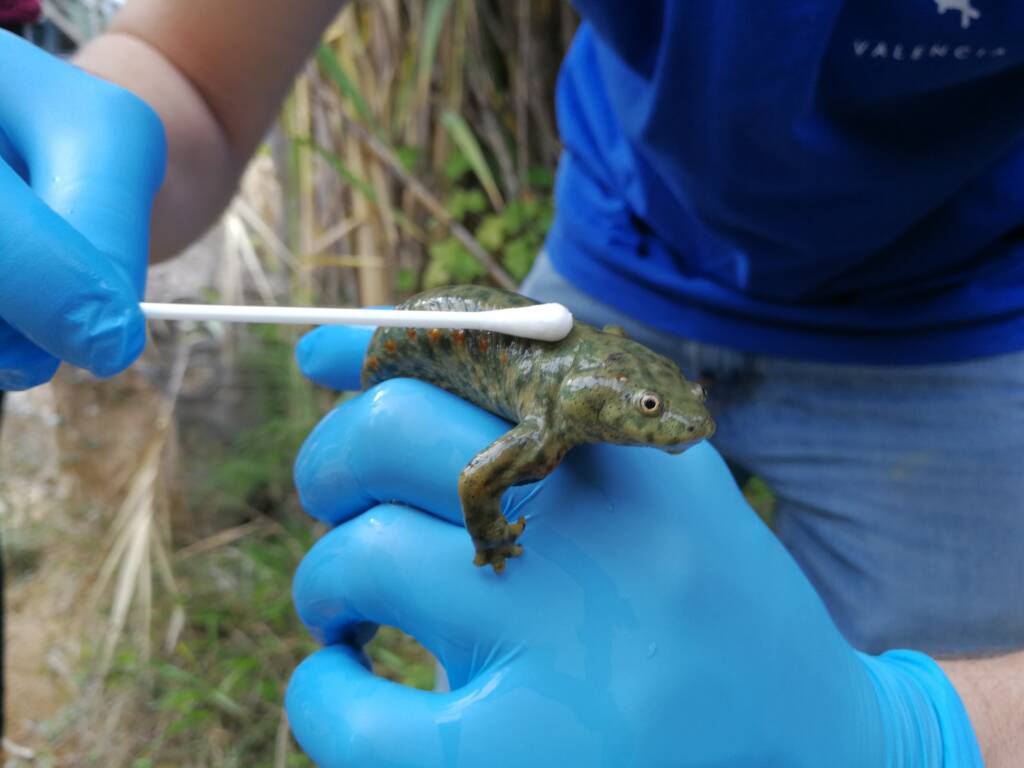
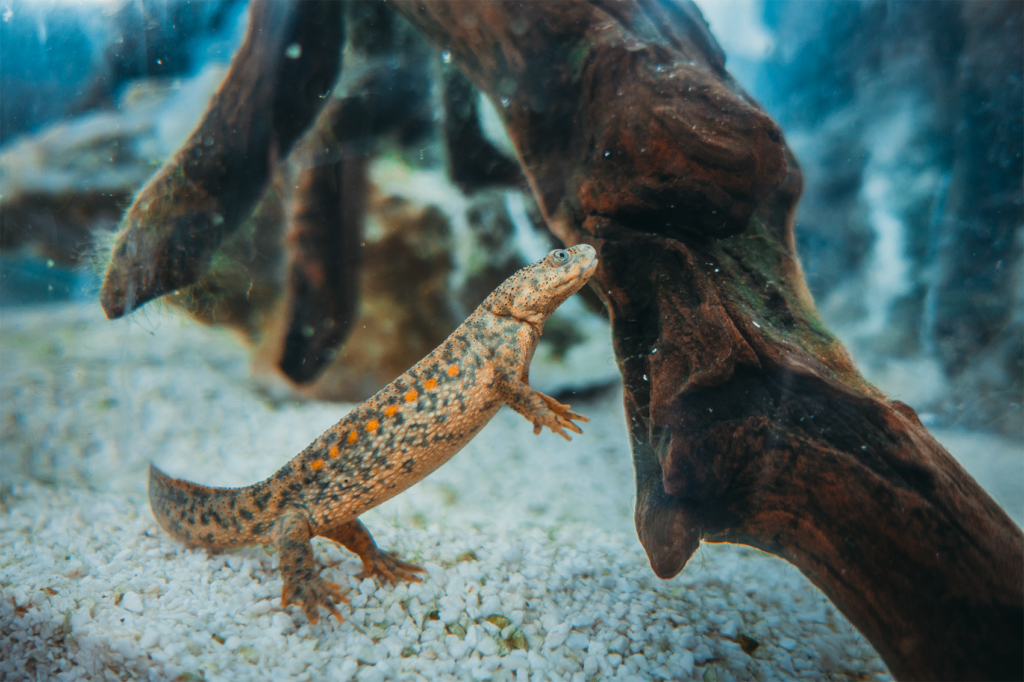
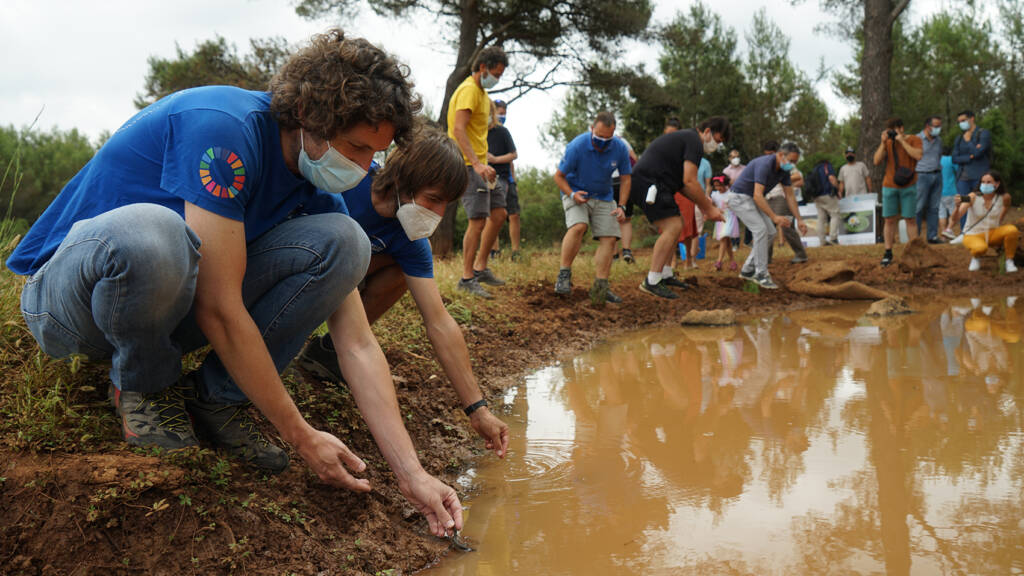
Monitoring of local amphibian populations in the Valencian Community
Amphibians represent one of the most threatened vertebrate groups, with almost 40% of the more than 7,000 species described included in threat categories by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
The main causes of this worrying situation include habitat loss and deterioration, climate change, environmental pollution, invasive species, and disease transmission.
This line of action focuses on monitoring populations of various amphibian species at strategic points in the Valencian Community. The objective is to analyze population trends, monitor areas previously affected by high mortality rates, determine possible causes of regression, and establish responses to mortality episodes.







-
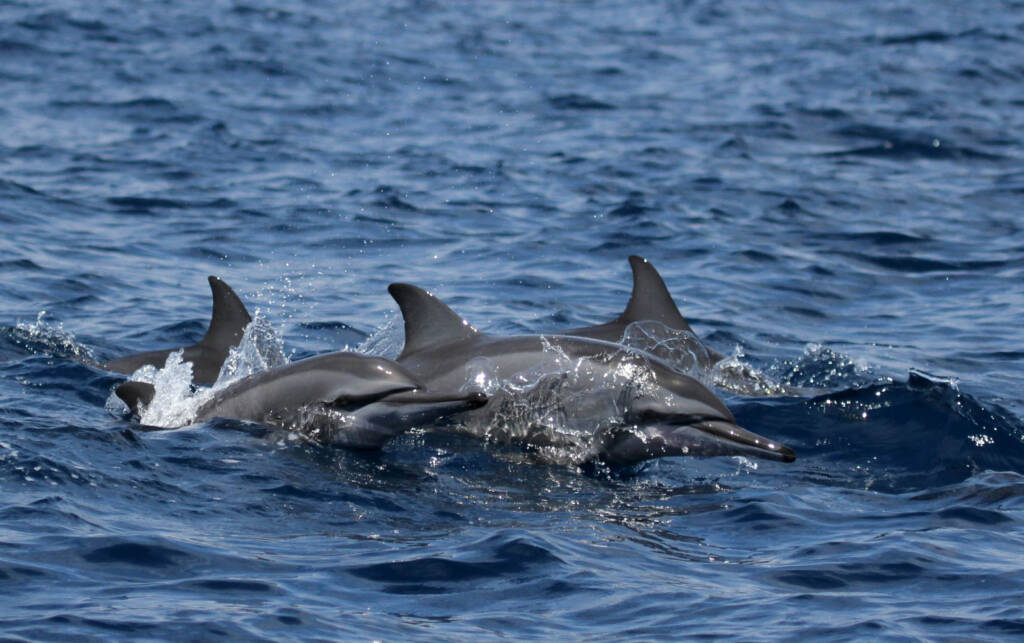
Rescue and health assessment of bottlenose dolphins in the Almadraba of Murcia
The aim is to work with bottlenose dolphins that accidentally enter the Almadraba of La Azohía in Murcia. This incident is used to carry out a complete evaluation of the health status of the animals, ensuring their proper handling and release. The Almadraba, a seasonal art, generally focuses on capturing pelagic species, such as bluefin tuna and smaller tunas.
Given its selectivity and proximity to the coast, only a portion of the population can be captured, allowing the release of species that are not the subject of study. Although bottlenose dolphins are occasionally found in the Almadraba nets, proper handling by Almadraba personnel minimizes the impact on these animals, which occurs rarely throughout the year.

-
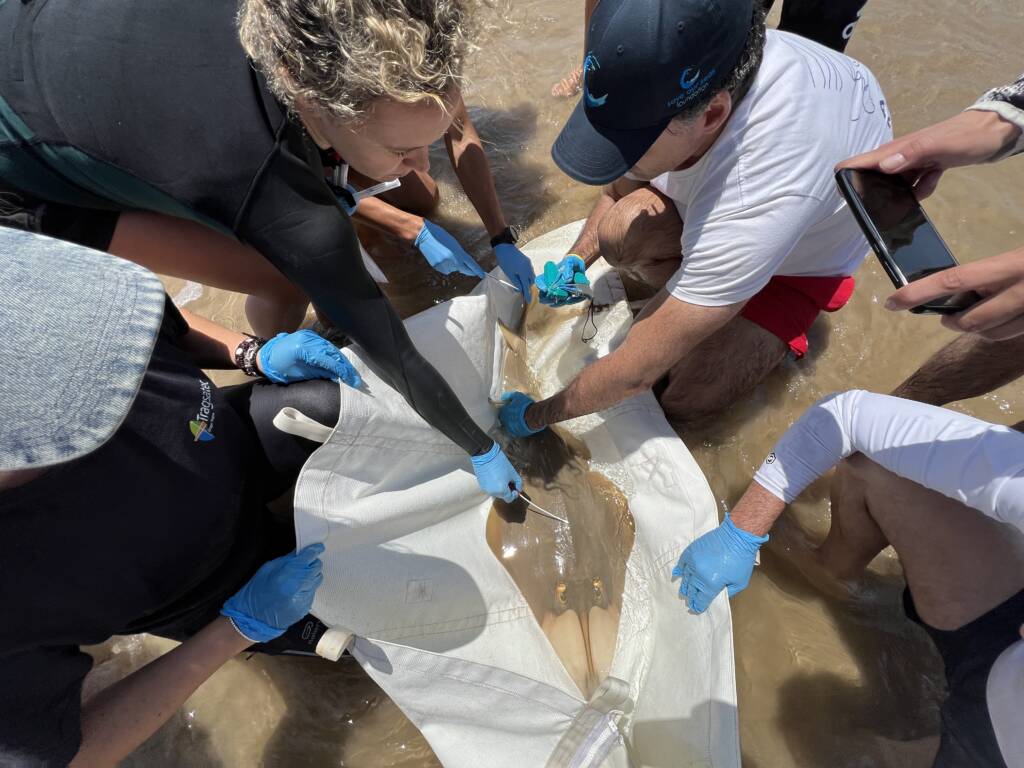
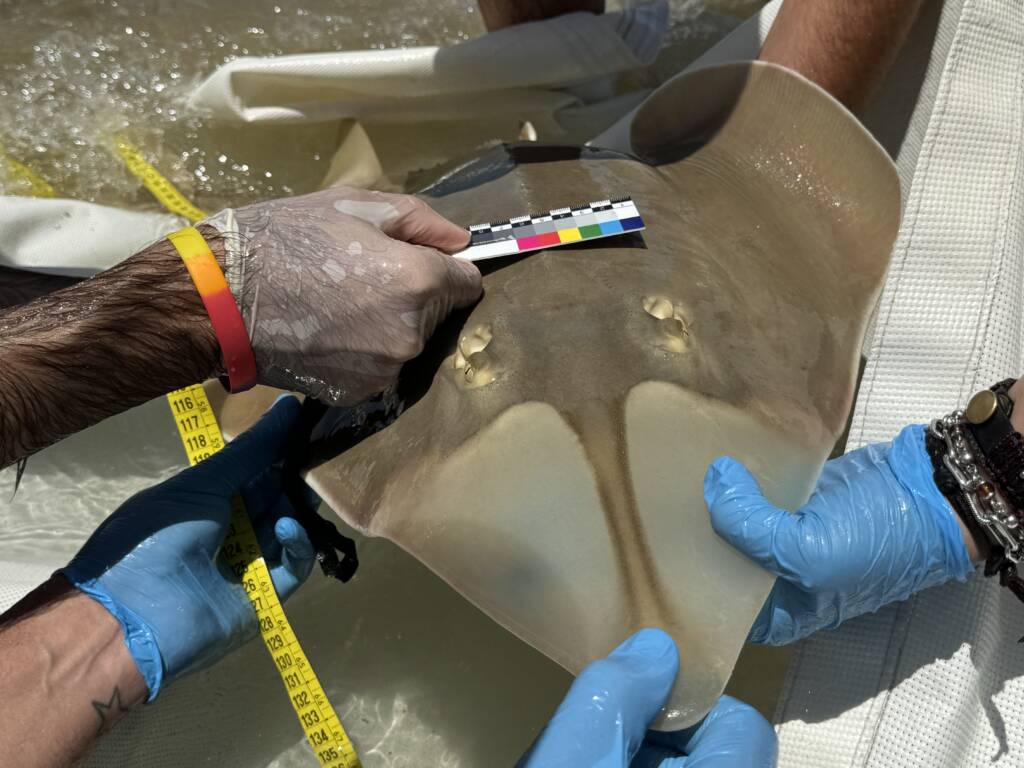
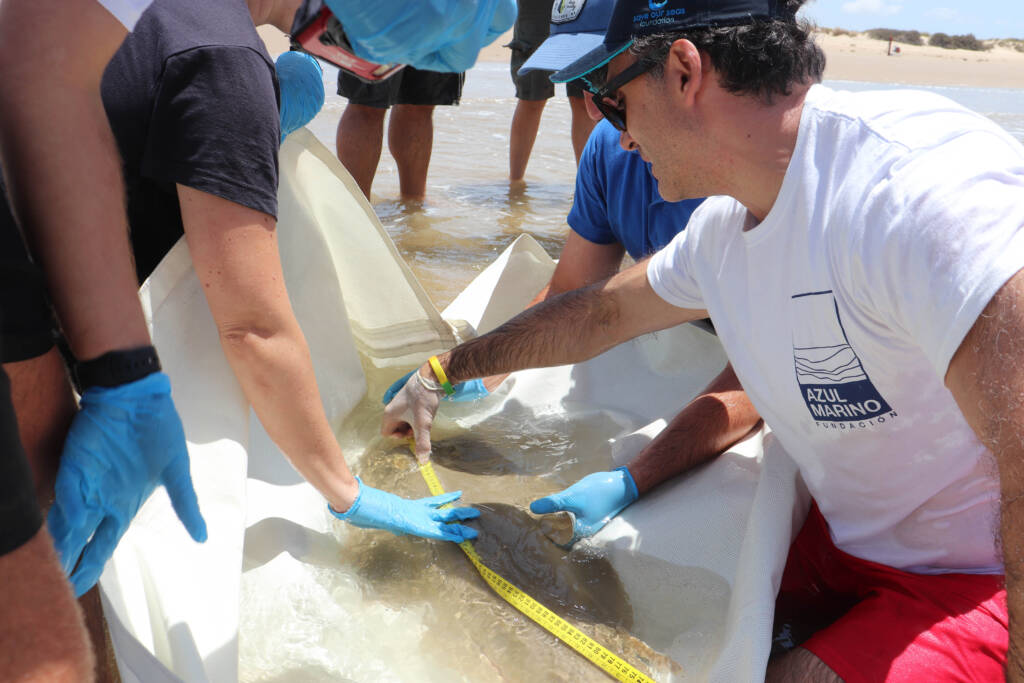
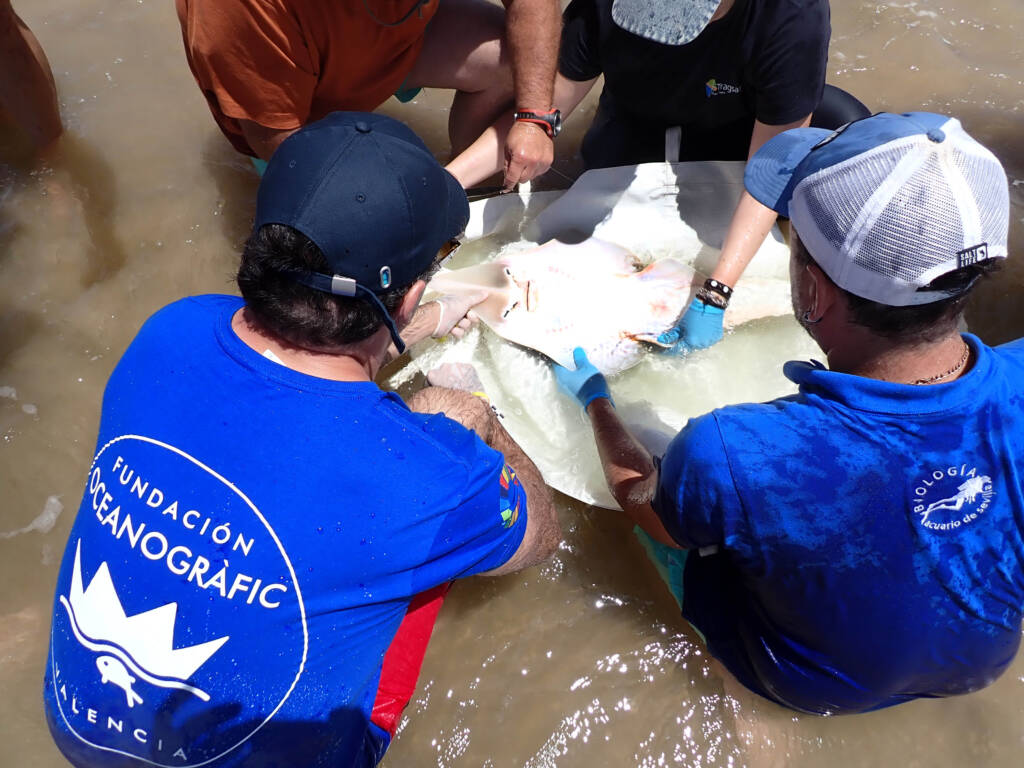
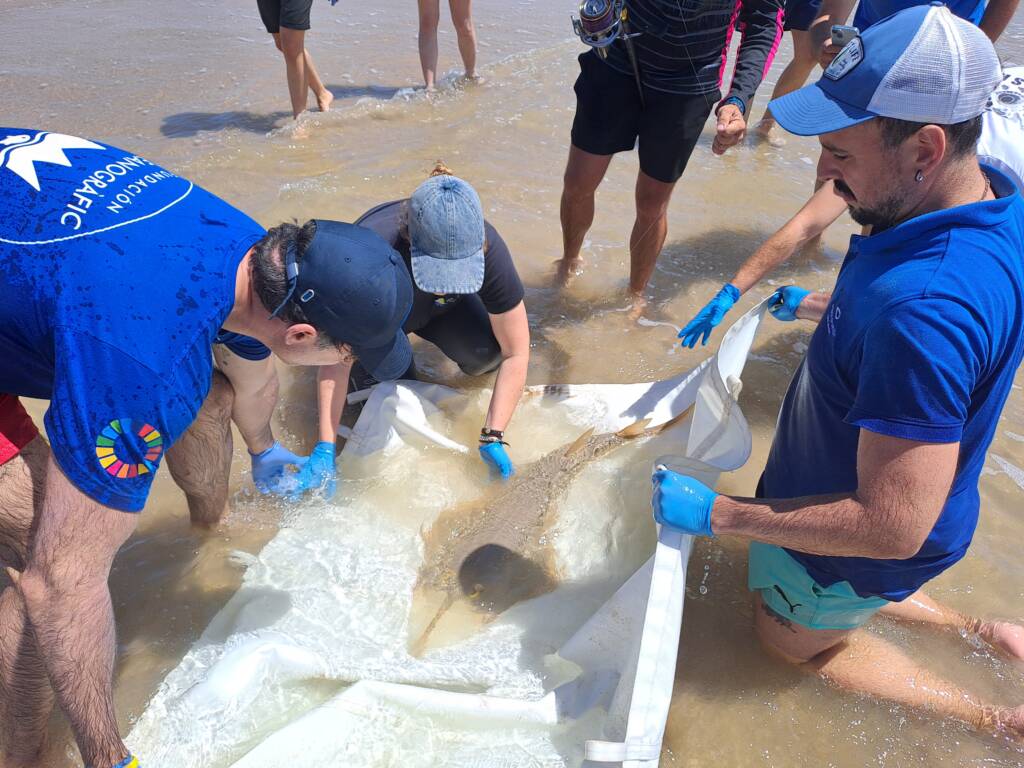
Monitoring and census of the guitarfish in Doñana National Park and other regions of Andalusia
Los peces guitarra gigantes se han convertido en una de las especies marinas más amenazadas, siendo la especie Glaucostegus cemiculus especialmente crítica en aguas europeas y del Mediterráneo.
En colaboración con la Associació LAMNA, la Fundación Oceanogràfic ha recopilado datos cruciales a través del proyecto de ciencia ciudadana MECO, identificando capturas y grandes agregaciones en las costas de Huelva y Cádiz. Un estudio preliminar en el Parque Natural de Doñana certifica su presencia y brinda la oportunidad de investigar si constituye una población estable o un punto crucial para los juveniles, ofreciendo esperanzas para la gestión y conservación futura de la especie.
Los objetivos de esta línea son evaluar la presencia y el estado poblacional del pez guitarra gigante en aguas de Doñana, describir las agregaciones en aguas someras durante mayo y junio, y comprender el parentesco entre poblaciones existentes y ejemplares en cautividad para planificar un proyecto de recuperación ex situ.





-
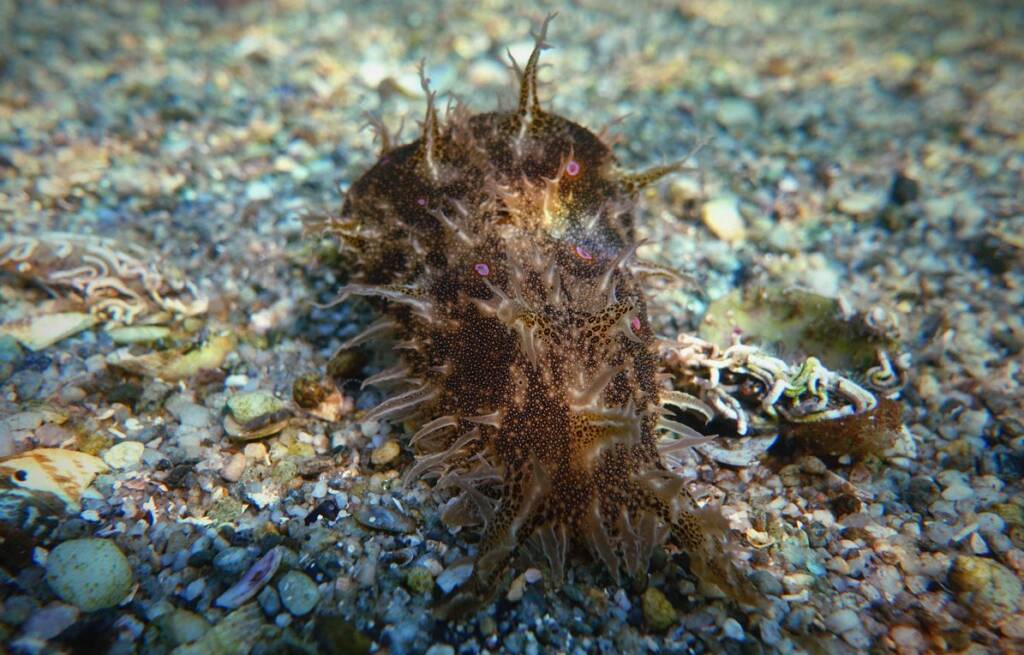
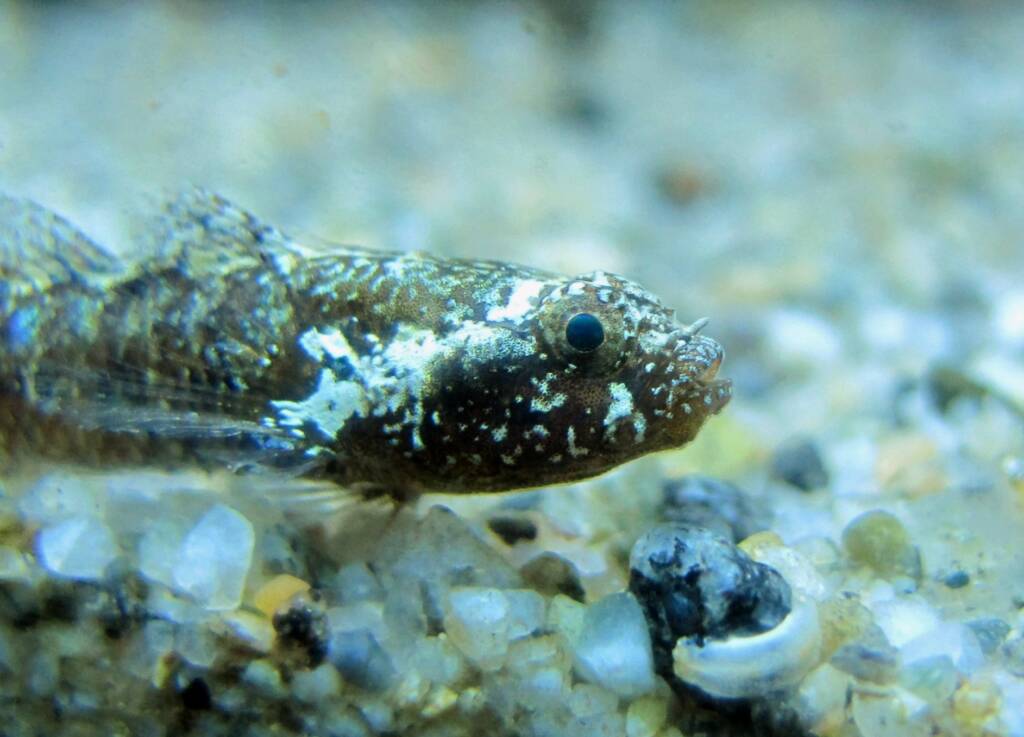
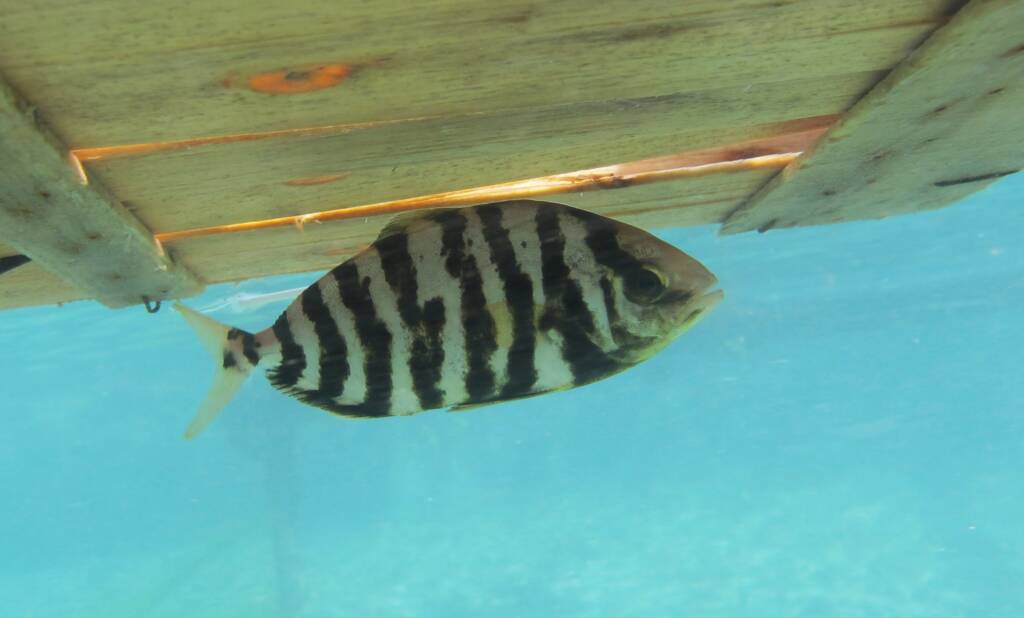
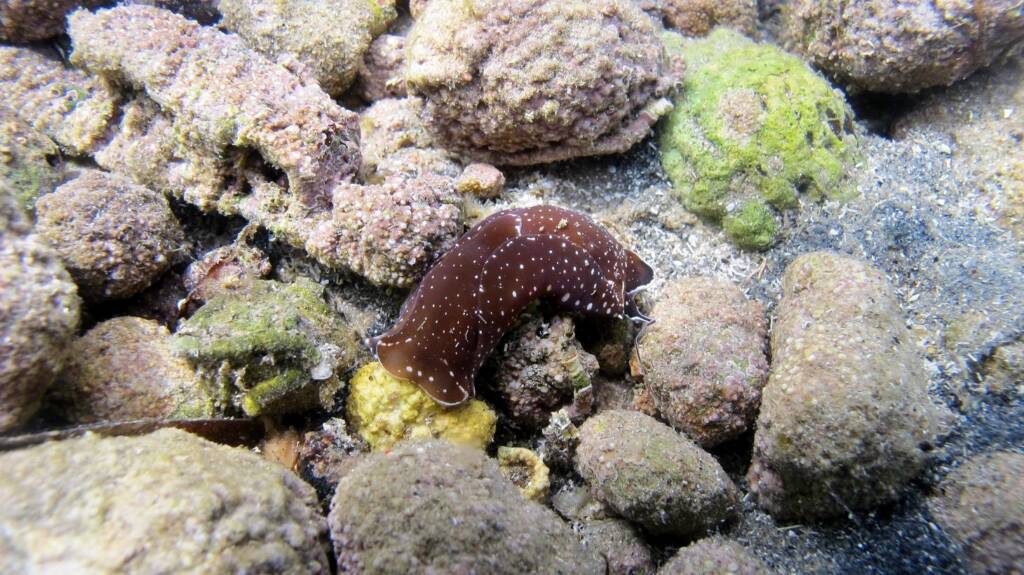
Monitoring and control of rare and invasive species
Esta línea aborda el desafío actual de la colonización de organismos marinos procedentes de ecosistemas lejanos.
Facilitada por el tráfico marítimo y el cambio climático, esta colonización plantea riesgos para el equilibrio ecológico al competir con especies autóctonas y alterar las dinámicas de la biodiversidad.
Los objetivos clave de esta línea de actuación son la identificación y el registro de organismos invasores, especialmente peces, crustáceos e invertebrados externos al Mediterráneo; desarrollar una base de datos de estas especies y estudiar su distribución para evaluar el desplazamiento potencias de los nichos ecológicos y los riesgos que puede suponer para la biodiversidad local.
La colaboración ciudadana, en particular pescadores, buceadores y personas que frecuentan las costas, es fundamental para recopilar observaciones y datos relevantes.





-
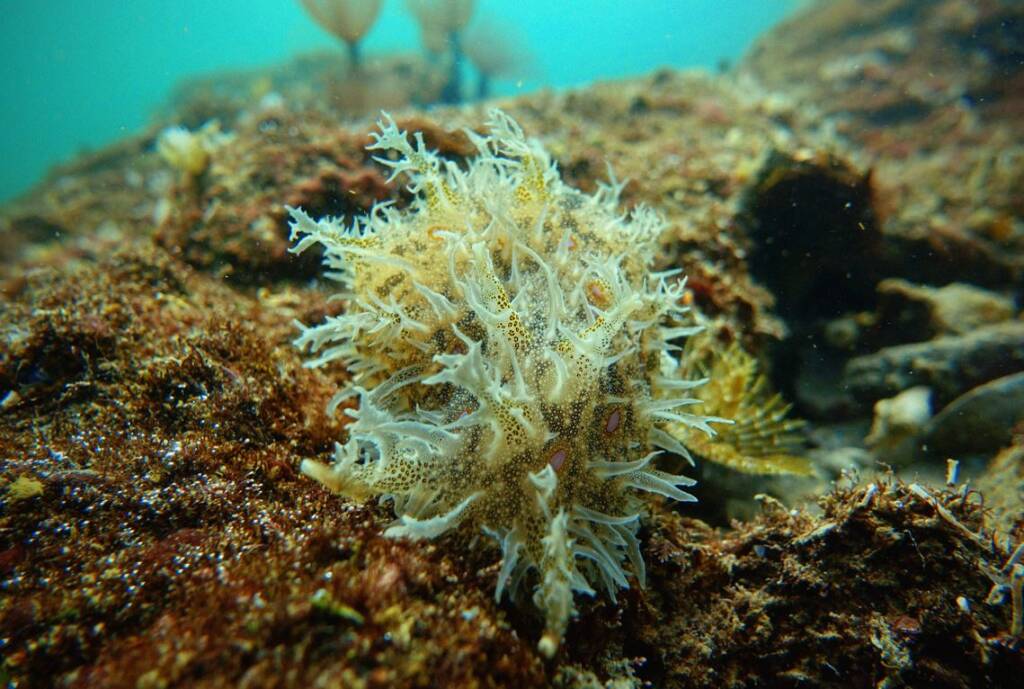
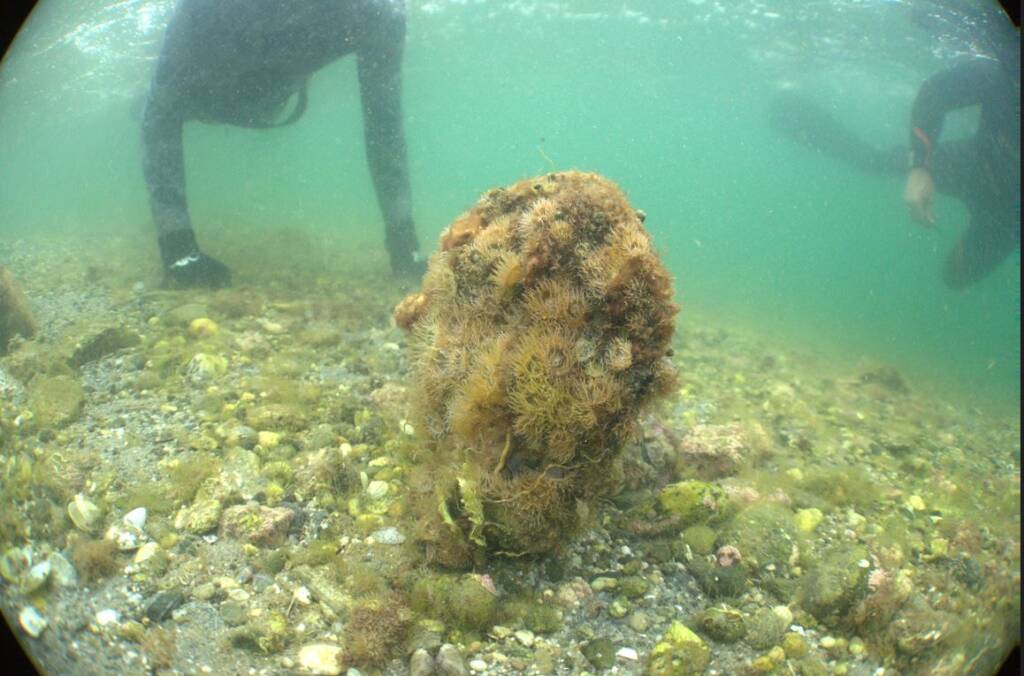
Control of critically endangered species: Pinna nobilis and Pinna rudis
La línea de control de especies gravemente amenazadas, como la nacra (Pinna nobilis) y su pariente Pinna rudis, se centra en abordar el impacto de un protozoo patógeno que ha afectado drásticamente las poblaciones de Pinna nobilis en el Mar Mediterráneo desde 2016.
Este evento de mortalidad masiva se suma a otras amenazas previas como la contaminación, la pesca y la degradación del hábitat, llevando a la UICN a catalogar a la nacra como una especie en peligro crítico.
La línea de actuación se centra en el seguimiento de poblaciones existentes, la creación de una red de observadores y la identificación de soluciones para combatir esta amenaza.
Los objetivos clave incluyen el estudio de la distribución de Pinna nobilis y Pinna rudis en la costa norte de Sicilia, el seguimiento de poblaciones en la Reserva Marina de Capo Peloro (Sicilia) y la continuación del proyecto “Red Trasmediterránea de Colectores de Larvas de Nacra” para acciones de reclutamiento larvario y recolección de juveniles.
Estos esfuerzos se realizan en colaboración con expertos científicos para diseñar protocolos replicables y sostenibles para la cría y mantenimiento, y para evaluar la posible expansión de Pinna rudis en el Mediterráneo.



-
Monitoring and care of manta rays and other marine species in key locations of the Valencian Community
Esta línea se enfoca en la monitorización de la fauna íctica, especialmente las mantelinas (Gymnura altavela), catalogadas como En Peligro Crítico en el Mediterráneo por la IUCN.
Este esfuerzo colaborativo con la Associació LAMNA se centra en determinar y evaluar el estado de la biodiversidad en áreas específicas, desarrollar protocolos de censo visual y proponer programas de seguimiento para las comunidades biológicas.
Además, se aprovecharán los transectos para producir fotos y videos que aumenten el conocimiento y sensibilicen a la ciudadanía sobre la importancia del respetar el ecosistema marino para su conservación.
La FAO y la UNESCO respaldan este enfoque en un momento crucial para el cuidado y preservación de la naturaleza.
-
Exploration of the deep ocean
Esta línea tiene como objetivo superar los desafíos asociados con la inaccesibilidad y las condiciones extremas del océano profundo.
La exploración del océano por debajo de los 200 metros de profundidad sigue siendo un desafío debido a las condiciones físicas y al alto coste económico.
Esta línea de actuación, en colaboración con el doctor Nathan Robinson, busca desarrollar metodologías precisas y eficientes para la exploración y la captación de imágenes de la biodiversidad del océano.
Los objetivos y fases clave incluyen la definición e implementación de un sistema de captación de imágenes adaptado a las condiciones ópticas y adaptativas del océano profundo (200-1000 metros), el desarrollo del sistema de inmersión y la adaptación continua del sistema para maximizar su versatilidad y operatividad.
Other programs Conservation
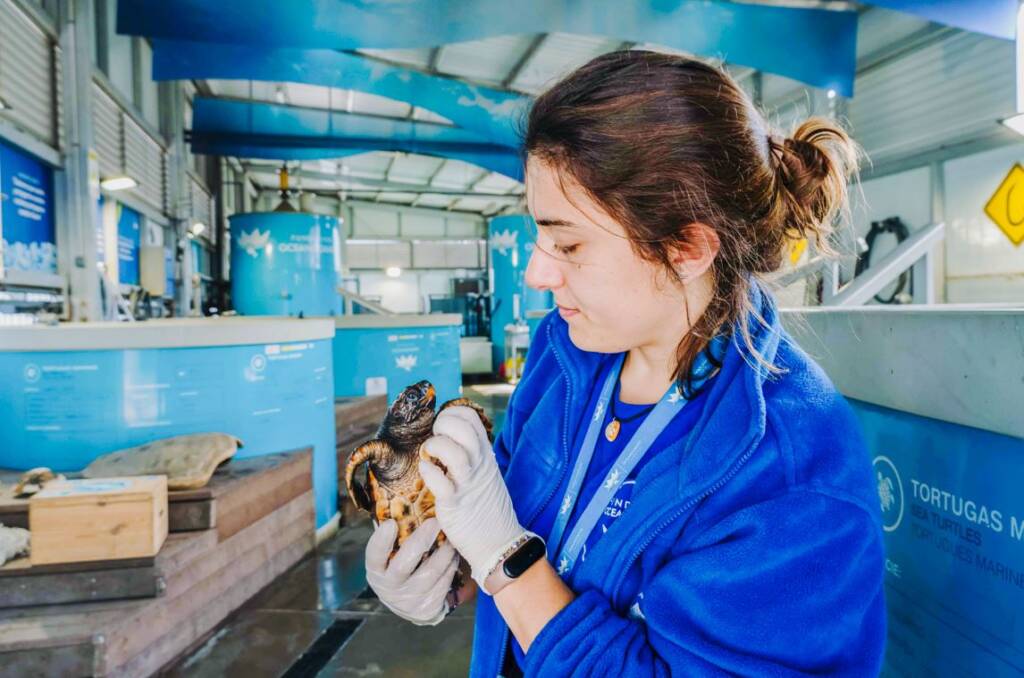

Marine Fauna Recovery Center
Marine Fauna Recovery Center
The rescue and recovery of injured animals helps the conservation and research of species This program…

Reinforcement of Endangered Species for Reintroduction
Reinforcement of Endangered Species for Reintroduction
Breeding species in controlled environments is a fundamental tool that helps to repopulate habitats This program…
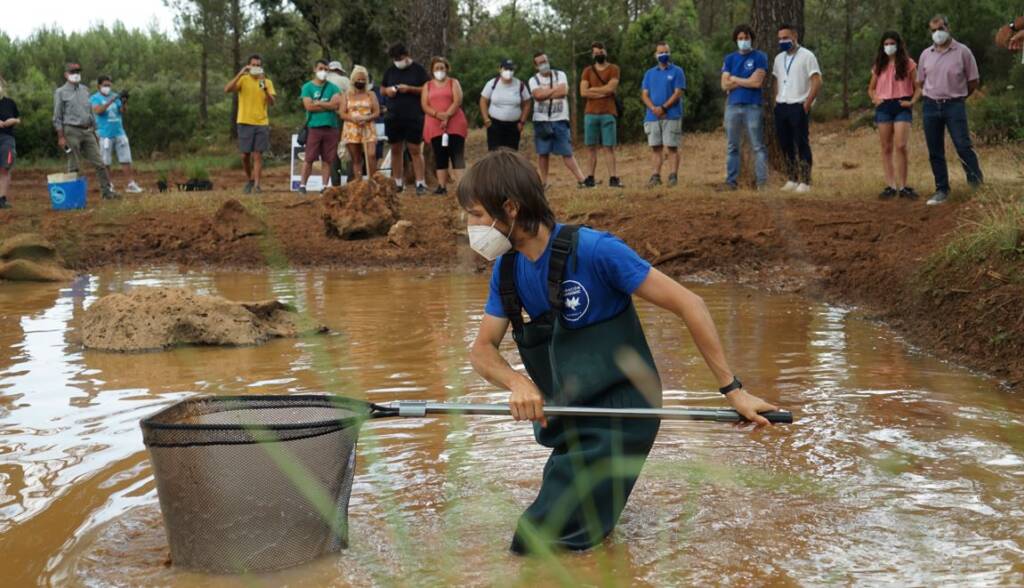

Habitat Restoration
Habitat Restoration
The restoration of affected habitats is essential to be able to reintroduce species Through various restoration…
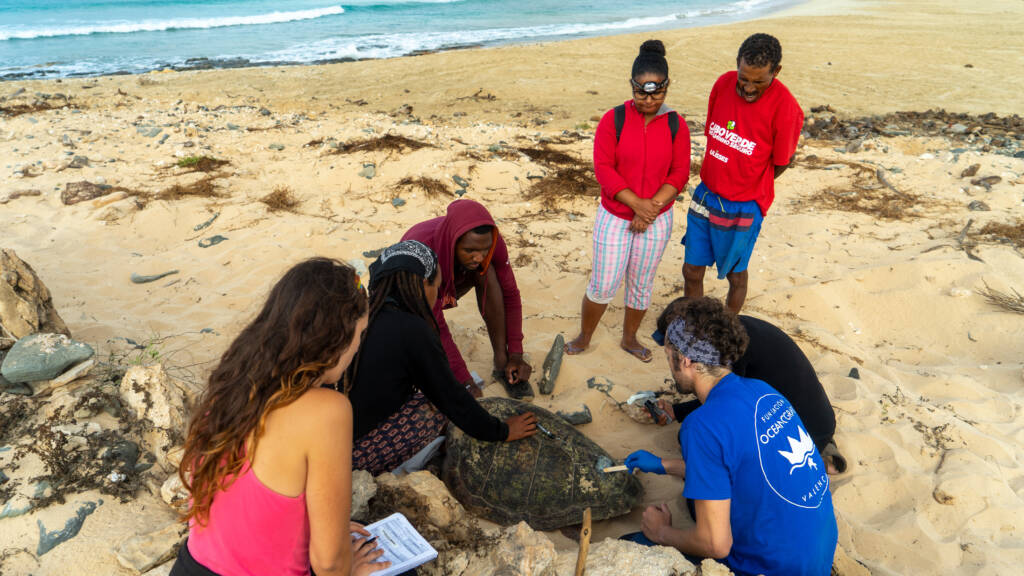

Professional Training and Knowledge Transfer
Professional Training and Knowledge Transfer
Strengthening capacities and collaborations around the world to protect marine fauna Our knowledge is shared nationally…

Oceanogràfic Sustainability
Oceanogràfic Sustainability
Reducing dependence on the marine environment It is common for modern aquariums to have breeding programs…

Generating a Forum for Discussion and Knowledge for Conservation
Generating a Forum for Discussion and Knowledge for Conservation
Promoting interdisciplinary discussion and exchange. The main objective is to position the Oceanogràfic as a driver…
